In Teulet et al. (Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022. 76:45–65), we reviewed the roles and impacts of T3SS on nitrogen-fixing associations between legumes and rhizobia.
Within the framework of a Master thesis, rhizobia were isolated from nodules of wild accessions of Lotus corniculatus that were collected across Western Switzerland. To gather the greatest diversity of strains possible, sampling sites were selected across an East-West transect, at diverse altitudes and on both sides of the Alps.
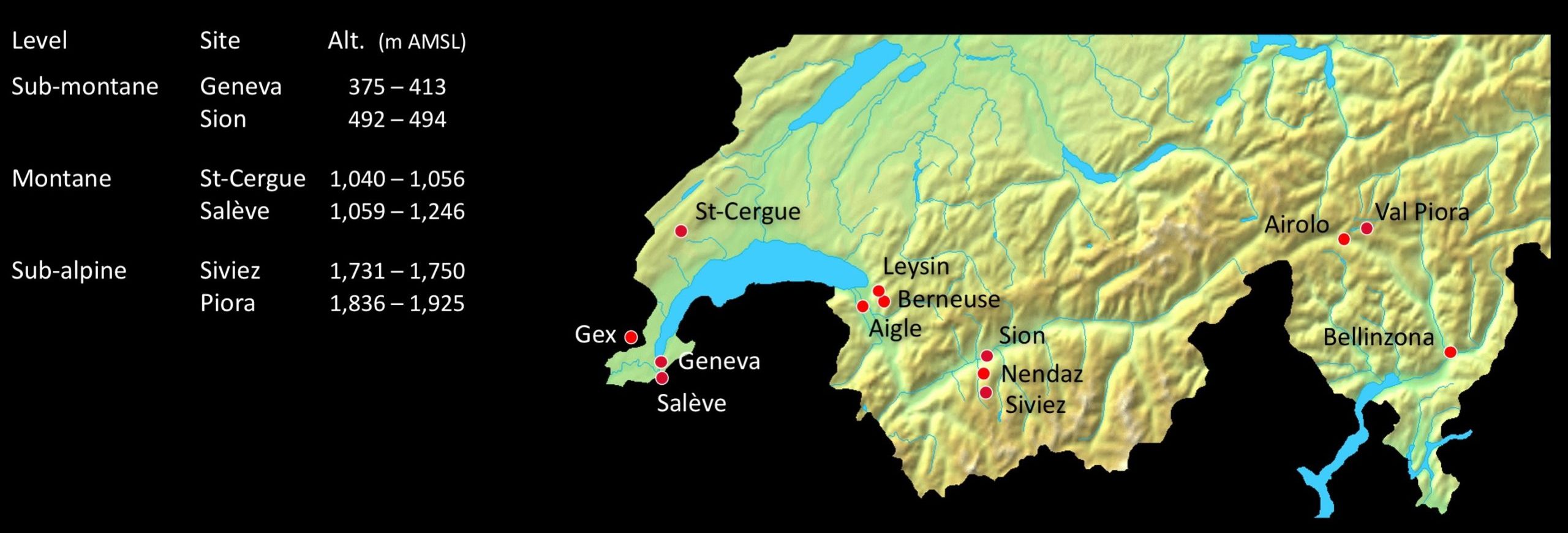
More than 100 rhizobia strains were characterized at the molecular level by sequencing their rpoB gene and by MALTI-TOF mass spectrometry. These analyses revealed a surprinsingly large diversity of microsymbionts in all of the soils that we probed.
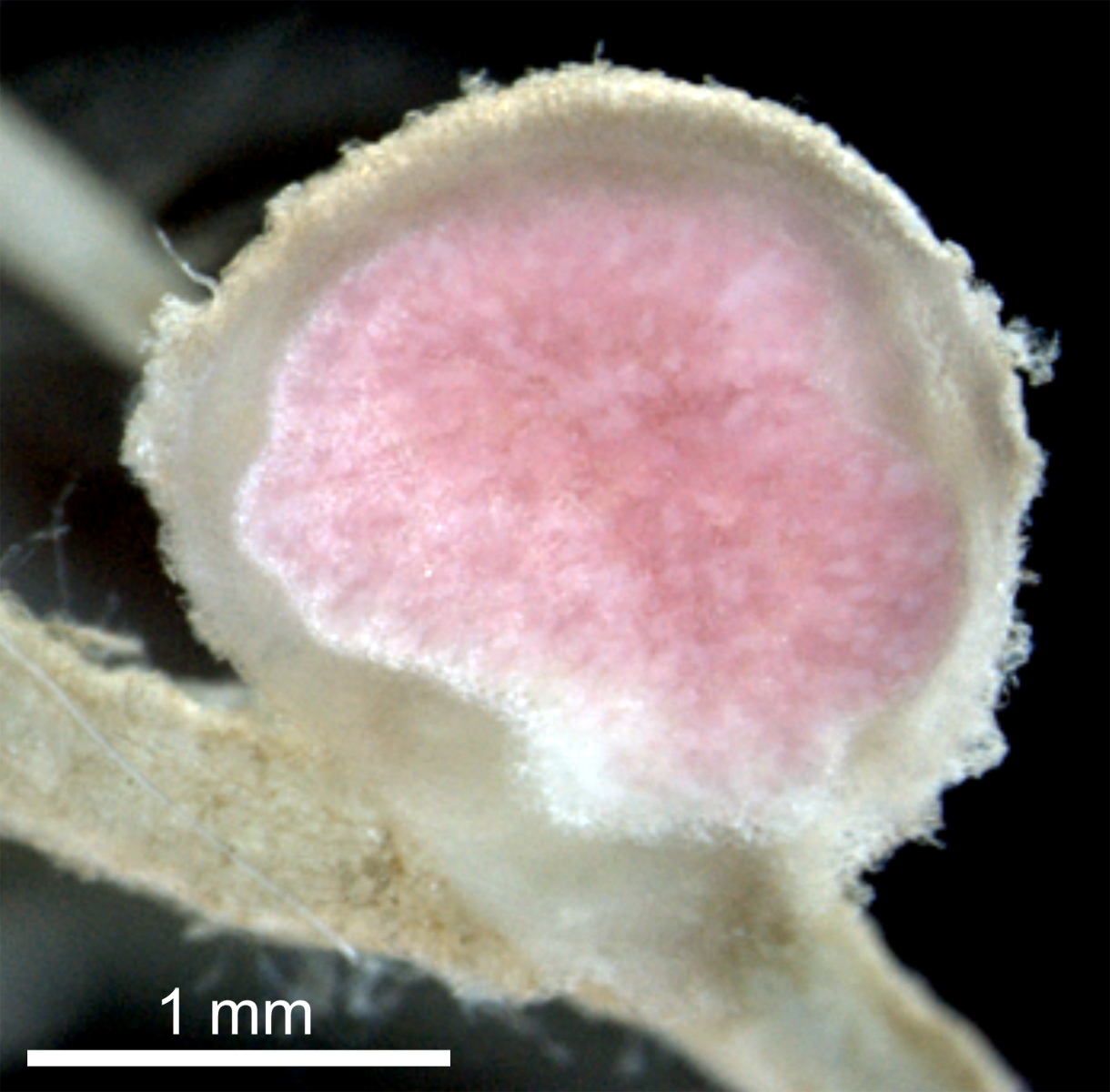
Then representative isolates of the diverse phyla of mesorhizobia identified molecularly were inoculated on diverse cultivars of L. corniculatus. Symbiotic proficiency of the strains varied from poor nodulators and nitrogen fixers to fully proficient strains.



